The Internet of Things (IoT) is the physical devices that are connected to the Internet, billions of which are now around the world. While still in its relative infancy, IoT offers significant potential for the future.
In 2023, the growth rate for IoT was 15 per cent and is projected to maintain a steady annual growth of 17 per cent until 2030. Helped along by wireless signals, inexpensive computer chips and the paramount expansion of AI, IoT continues to grow and develop. From robot assistants that provide information to stoves and washing machines that people can control through phone apps, IoT is becoming a part of daily life.
Data scientists can play a crucial role in extracting meaning from IoT. Today, data scientists can take and use the data collected through technologies like IoT and transform it through analysis and visualisation so that it can drive value for an organisation or business.
For future data science leaders, understanding technologies such as IoT can bolster their decision-making and improve business outcomes.
Below, we’ll look at what the Internet of Things is, where it comes from, how it is being used, its impact on different sectors and its potential effect on the future.
What is the Internet of Things?
Around the world, devices are linked via the internet and can communicate with one another. These devices and their online connectivity make up the Internet of Things.
Those who have an Amazon Alexa or Google Home device in their homes are tied to IoT. Sensors in these devices enable them to communicate with one another.
It is now possible for someone to turn on the lights at home, even from a distance or to start up a car in the driveway from inside while grabbing a coat.
When devices are connected to IoT, they can process spoken commands or commands that people give them through an app. Users can even create a routine for Alexa to report the weather when it hears a morning greeting or preheating the oven through a phone app.
Turning on lights, protecting homes with security services like Ring cameras and creating experiences that were not possible before are all taking place thanks to IoT.
How does the Internet of Things work?
The Internet of Things is technically similar to computers and other devices in that they are all connected to the internet and its vast sources of information. When asking a Google Home device a question or using an iPhone to ask Siri a question, the devices access the internet to get the right answers.
The widespread nature of the internet is a big part of what makes IoT possible. The other reason that IoT is now so easy to access is the availability of cheap computer chips. Computers used to be large, cumbersome and extremely expensive. In the early days, they even needed special rooms to contain their “brains”.
The smaller and less costly the chips became, the more easily they could be brought into people’s homes and businesses. Now, computer chips cost very little and the internet is nearly everywhere. That makes it extremely easy to purchase IoT devices and get them up and running.
IoT devices share data via sensors and the cloud. Sensors receive physical input and use the internet to take an action or communicate with another source.
Common examples are:
- the microphone in a Google Home device
- a temperature gauge that monitors an industrial boiler and sends data to a control system
- a blood pressure monitor that submits information to a medical provider
Much like Google Docs or other programs in which information created in them is stored off-site in a cloud-based fashion, IoT devices store and access knowledge and routines in the cloud, and use their sensors to understand what is being asked of them. That, in turn, tells them what response to produce.
IoT devices may seem intelligent, but in reality, they are simply responding to set inputs and variables with predetermined information. They can be quite useful and valuable, as well as enjoyable, but they do not think and understand as people do when they provide information.
What are Internet of Things devices and how is the Internet of Things being used today?
IoT is making devices smarter and is responsible for innovative changes in many industries. Internet of Things devices are everything from an Amazon Echo in the home to the sensors on a drawbridge that alert the operator to an approaching ship.
Some smart devices help companies with shipping and logistics, and some vehicles can drive themselves. All of them are connected to the Internet of Things and the number of devices connected will not slow down anytime soon.
While these devices are beneficial in many ways, it is important to remember that they are always collecting and storing information. A Google Home device is always listening to hear its “wake word”, smart TVs know what shows people watch and video doorbells can identify who visits a house.
Most of the time, this is harmless, but security issues need to be considered. The more devices connected to IoT, the greater the potential for security breaches and related problems. Still, using IoT devices provide significant benefits in many areas of life.
Today, the Internet of Things is being used in some amazing ways, including:
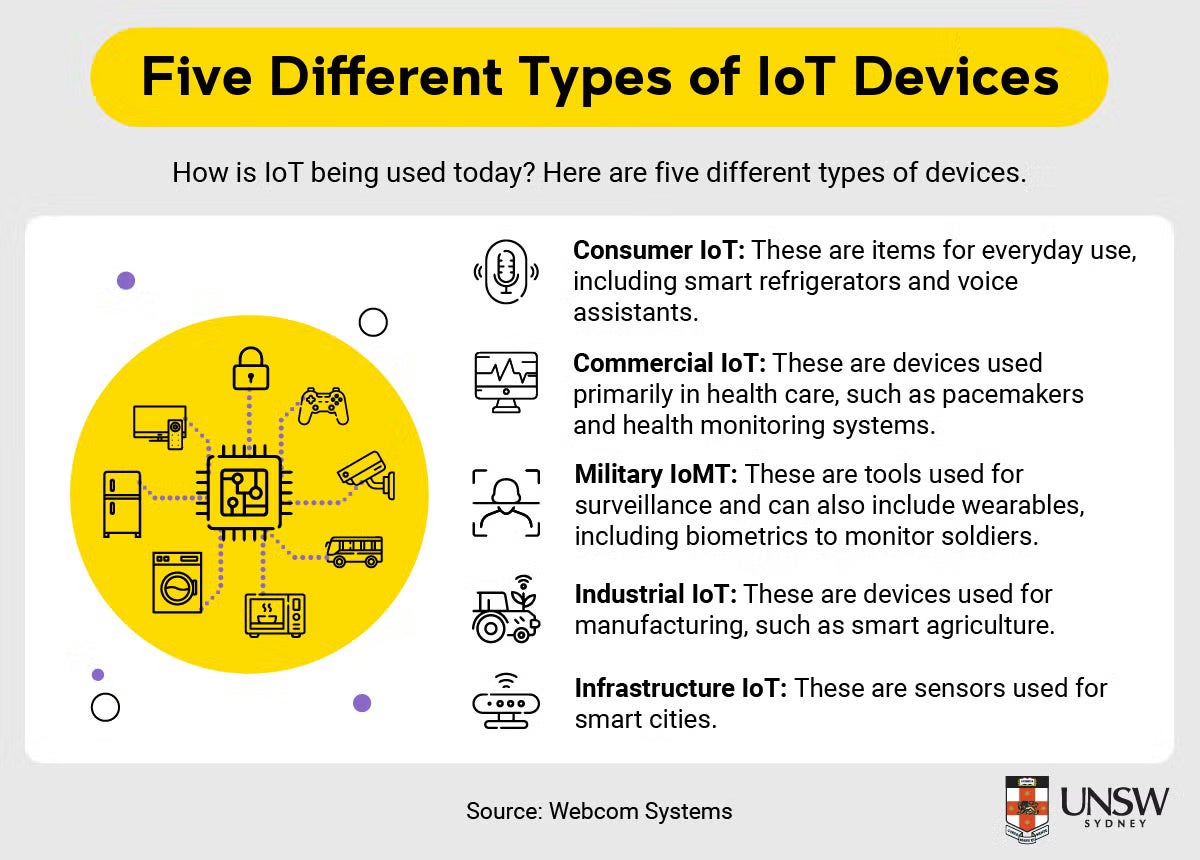
Consumer IoT
Consumer IoT includes everything from the smart devices in a home – such as light bulbs, TVs, appliances and voice assistants like Alexa – to the connected technology in today’s vehicles. Consumers have access to all kinds of devices to make their lives easier and more convenient.
Commercial IoT
In large chain stores, IoT is used to scan for theft, correct pricing problems and track inventory. Items that are running low can be automatically reordered and anything that does not arrive as planned sends a message so a human can address the issue. IoT devices are radically changing shipping and logistics.
Military IoT
For security reasons, the military tends to be quieter about its IoT use – called IoMT, or Internet of Military Things. However, autonomous aerial drones, robots, munitions and armour are all examples of IoT devices currently being deployed.
Industrial IoT
In industrial settings, IoT devices are now being used to advance assembly lines, automate production processes and make life easier and safer for the people working in those environments. From robotic options to detailed sensor information, IoT is helping industries thrive.
Infrastructure IoT
Connecting infrastructure to IoT can be crucial to improving safety and security. IoT-connected cars can brake on their own when they sense an object ahead of them. Positive Train Control systems can slow passenger trains for curves to reduce the risk of derailment. Cameras in city buses and other vehicles can alert authorities to crimes, dangerous driving or accidents. The more IoT devices are used in infrastructure, the more complete and secure that infrastructure can become.
What is the impact of IoT in different sectors?
From infrastructure in large cities to the increasing development of artificial intelligence (AI) for home and business use, IoT and its devices are causing big changes in how people handle life.
Some sectors have been affected more than others, while other areas may catch up in time as new devices are developed.
Transportation
Cars, trains, trucks and buses are all travelling on roads that are increasingly fitted with sensors. Aside from communicating with vehicles, these sensors can notify maintenance crews or authorities of issues. Additionally, transportation logistics are affected by the tracking of shipment locations and how the shipments are handled and processed during their journey.
Smart infrastructure
Cars, homes and even cities are all becoming part of smart infrastructure, thanks to IoT devices. Smart homes today can be designed to be almost entirely controlled by apps and voice commands. Cars can drive themselves on many roads and even those that do not drive themselves can alert drivers to lane drift, speed and brake.
Cities are using IoT to track population movement, track cars that run red lights and track whether city buses are obeying the speed limit, among other functions.
Security
There are numerous application opportunities for IoT in the security industry, such as Ring cameras and smart locks. IoT-connected cameras in commercial vehicles can also reduce theft and tracking devices can ensure safe speeds, and protect drivers and pedestrians.
Security is a big concern for many people who study IoT devices. These devices have been hacked and cyber attacks are likely to increase. While security professionals can use IoT devices for their own needs, they also have to be clear on the inherent risks of devices that are connected to the cloud.
Privacy
Because of how IoT works, privacy is a complicated issue. Most consumers understand that they are trading some of their privacy away to receive a more convenient experience. Usually, that does not produce any kind of serious risk. However, the makers of IoT devices are harvesting a lot of data and are likely selling it, which means that it’s a sector IoT can tap into.
Cyber warfare
Cybercriminals are on the rise and their crimes are getting more serious. If they can hack into a computer, home, car, power grid or another device operated through the internet, they can potentially control it. That can mean that they would not only be collecting data but also using it to make changes to other IoT devices on the same network.
Big data analytics
Big data is only getting bigger. The amount of information being collected about people as they go about their lives is staggering. IoT devices are constantly collecting data, which can provide valuable big data insights.
AI
AI can help people who need additional assistance due to a disability, such as an inability to see or operate systems in their homes. It can also operate machinery in areas where it is not safe for humans to do so, and provide chatbots and other support for websites and online experiences.
What are the benefits of IoT?
While IoT and connected devices may have inherent security risks, they also provide a significant level of benefits. Advancing the value of IoT will mean expanding on benefits that help the greatest number of consumers and businesses.
Benefits of IoT for business
In the business world, IoT is being used to provide more value and benefits for companies. The biggest benefits that companies see include the following:
- Increased productivity as technology takes over tasks and frees workers up for other areas.
- Improved security for a company, its online presence, and its shipping and logistics needs.
- Improved customer service and customer experiences through AI support and information.
- More networking opportunities for companies to connect with suppliers and distributors.
- Reduced expenses due to improved efficiency.
Benefits of IoT for consumers
IoT devices do not just offer advantages to businesses. Consumers are also reaping benefits from how IoT is changing their lives. The value that customers are seeing includes the following:
- Convenience through smart home devices, faster interactions with companies and support for tracking purchases from suppliers.
- Ease of returning items, procuring parts for repairs or replacing items through the use of chatbots and other AI-based options.
- Efficiency gains as they accomplish more when routine tasks are automated.
- Decision-making support through providing information efficiently, allowing customers to quickly compare their options and choose the best one for their needs.
- Improved safety and security from video doorbells, phone alerts from security companies, exterior cameras and other devices.
Future of IoT
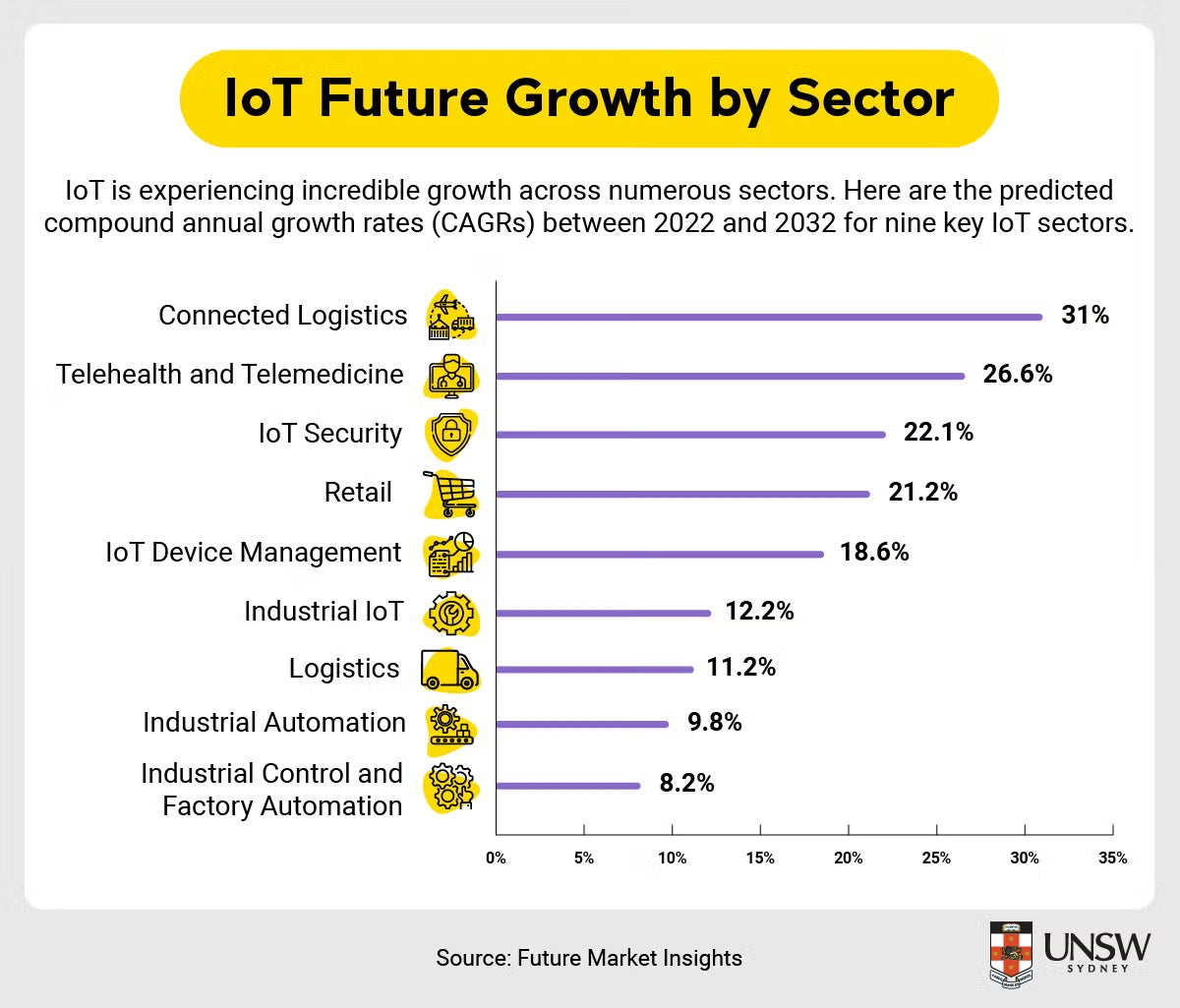
The future of IoT and its devices is bright. Overall growth projections for IoT are strong and the estimated compound annual growth rate (CAGR) in industrial IoT between 2023 and 2033 is an impressive 12.1 per cent. That means that it will reach a projected market value of $A2.09 trillion ($US1.39 trillion).
Growth projections in other IoT sectors are similar, with trends moving in an upward direction by high single-digit or low double-digit percentages. However, while the advent of IoT may seem like an overnight success, its growth took years of planning and development.
Now that that infrastructure has been laid, the continued growth and development of IoT will centre on innovative devices and applications. Where IoT will be in 10 years is hard to predict simply because so many technological breakthroughs are possible.
Below are five of the strongest future trends in IoT.
Growth in AI technology
The development of AI technology has expanded what companies and consumers can do and made it easier to perform tasks efficiently. As AI becomes more intelligent, it will make its way into more areas of life.
IoT connectivity with 5G and satellites
Today, IoT relies on internet signals (Wi-Fi). Devices that work through 5G cellular broadband and satellites experience faster, more secure connectivity with a higher level of stability than ever before. Self-driving vehicles, AI-enabled robots in factories and smart grids that offer renewable energy will be just parts of the massive 5G ecosystem.
Low latency and edge computing
Computing with low latency – the length of time it takes for a packet of data to travel from one location to another – can accomplish more. As low latency and cloud computing become more common, the combination will increase speed for users everywhere, easing communication.
Wearables
Smartwatches can already track health metrics, provide readouts of text messages, play music, take phone calls and more. Wearable options and features will continue to expand in the years to come. Smart rings, for example, allow for contactless payments, receiving alerts and locking smart locks, while biosensors track and record medical information, such as step count, body posture and vital signs.
Smarter homes and cities
Homes that are controlled exclusively through apps or voice commands are coming and cities are not far behind. Adjusting traffic and street lights to control traffic flow and security, for example, are just two ways that smart technology and IoT can help cities improve.
Each trend offers the opportunity for expansion and development of something that is already provided. With these changes on the horizon, the growth in what IoT can do will be explosive. More people and businesses worldwide will continue to be connected and will rely on IoT for more functions in their daily lives and working environments.
The value of IoT will continue to grow
It is no secret that many people love what the IoT can do for them. The value of IoT devices and their connectivity will continue to expand as time goes on. There will not only be more devices but also more options and capabilities for those devices.
Right now, IoT and its devices are still in their infancy. As businesses recognise the potential and consumers realise the ways that they can make their lives easier, there will be more requests for IoT devices and more interest in developing them to do even more.
Where IoT will eventually end up remains unclear. Is there a point past which AI and IoT cannot go? Will privacy and security concerns become enough of a deterrent that people will avoid IoT devices and the convenience they offer? Those are questions that can only be answered with time, but the current interest in IoT devices indicates that the development of these devices and the purchase of them will continue for the foreseeable future.
Be the power behind business decisions
As the world of technology and data continues to change, ensure you are in demand for diverse roles – even those that have yet to be imagined.
At the University of New South Wales, we prepare future leaders in data science to shape the development and application of technologies. With UNSW Online’s Master of Data Science, you’ll be equipped with the skills to organise, identify, analyse and ultimately use data to inform strategies, redefine questions and find answers that make an impact.
Learn more about how UNSW Online’s Master of Data Science can help you enhance your career.